

A PREROUTING -i eth1 -p tcp -m tcp -dport 21 -j REDIRECT -to-ports 20021Īs you see, all requests from internal networ are redirected to "local" server and all others are redirected to "internet" server. I also added these strings to my iptables config: -A PREROUTING -i eth0 -p tcp -m tcp -dport 21 -j REDIRECT -to-ports 10021 These server processes listen to different ports (1001). I had the same problem with my pureftpd server and worked it around with launching two different addresses to announce (like MasqueradeAddress in your case) one for internal zone and one for external (external address is being staticaly NATed be ciso router). You are also using TLS, that's why the router may not be able to track the FTP connection. The use of secure certificate files ( RSA) for your FTP connections ensures that your server and desktop environment credentials never compromise while on a network.As far as I see, you are connecting to your internal ip (192.168.1.53) but the server gives its external IP (71.127.90.47) according to MasqueradeAddress directive. Your Linux server is now viable for file transfers through FTP.
#Filezilla linux passive download
The lst-user can now download and upload data from or to the “ ftp_directory”. You should be able to see the FTP directory we created earlier for user “ lst-user”. You will be met with an RSA certificate we created earlier for encrypting our FTP connection. Next, you need to enter your FTP server details and click connect. Launch FileZilla and navigate to Site Manager from the File menu as depicted on the screenshot.
#Filezilla linux passive install
Install FileZilla client on your Linux desktop environment. $ ftp server-IP-addressīefore testing our connection after RSA certificate installation, we should restart vsftpd again. The following screenshot demonstrates this prohibition. Rsa_private_key_file=/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.keyĪ user will now not be able to log in from the command line due to the newly implemented SSL rules on this configuration file. $ sudo nano /etc/vsftpd/nfĪdd the following entries to the above file and save it: rsa_cert_file=/etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.pem The FTP server needs to be aware of this created certificate location and details. $ sudo openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 185 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.key -out /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.pem In the following command, the day’s parameter should be an estimate of the duration you intend to use your FTP server or keep it active. It is a recommended security measure to ensure retained file integrity of each FTP-initiated file transfer. This step lets us create a vsftpd-oriented certificate file for encrypting all FTP connections between a remote server and a desktop environment. $ ftp server-IP-addressĬonnect to FTP User in Linux Configure VSFTPD with an SSL in Rocky Linux We will use the created FTP user ( lst-user) credentials to test our FTP access. Afterward, you will need to key in the ftp command followed by the IP address of your server. To achieve this objective, you should be in a Linux desktop operating system environment.
The next step is to test this FTP connection from the command line. $ sudo firewall-cmd -permanent -add-port=7000-7500/tcp $ sudo firewall-cmd -permanent -add-port=20-21/tcp

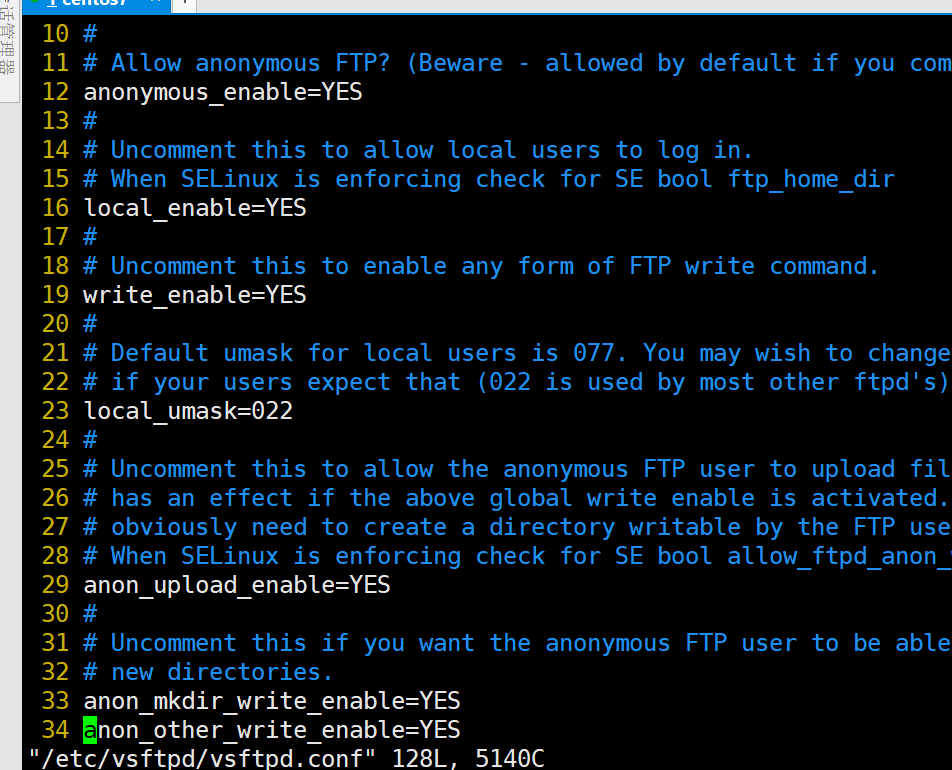
The system firewall needs to accommodate it together with port range “ 20-21” for FTP data and traffic respectfully. $ sudo systemctl restart vsftpdĬheck Vsftpd Status in Rocky Linux Open FTP Ports on Firewalldīased on the configurations we made in the “ /etc/vsftpd/nf” file, the port range “ 7000-7500” caters to vsftpd passive communication. We can now start and check the status of our initially enabled vsftpd service. Once the nf file is opened, make sure the file corresponds to the following line entry edits: anonymous_enable=NOĪdd the following entries. If you don’t have the nano or vi editors, install it with the command: $ sudo yum install nano Access its configuration file with the following command. We need certain vsftpd configuration settings enabled and others disabled. $ sudo bash -c 'echo lst-user > /etc/vsftpd/user_list' The final step is for the FTP server to recognize this user ( lst-user) in its “ user_list” file. $ sudo chown lst-user: /home/lst-user/ftp_directory $ sudo chmod -R 750 /home/lst-user/ftp_directory $ sudo mkdir -p /home/lst-user/ftp_directory
#Filezilla linux passive full
The user ( lst-user) now has full ownership of this directory on top of read, write, and execute privileges.

The created user needs to be associated with an FTP directory upon a successful login into the FTP server.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
